Mazda 6 Service Manual: Front brake (disc) inspection
Brake Judder Repair Hint
Description
Brake judder concern has the following 3 characteristics:
Steering wheel vibration
Steering wheel vibrates in the direction of its rotation. This characteristic is most noticeable when applying brakes at a vehicle speed of 100-140 km/h {62.1-86.8 mph}.
Floor vibration
When applying brakes, the vehicle body shakes back and forth. The seriousness of shake is not influenced by vehicle speed.
Brake pedal vibration
1. When applying brakes, a pulsating force tries to push the brake pad back occurs. The pulsation is transmitted to the brake pedal.
2. The following are the main possible causes of brake judder:
Due to an excessive runout (side-to-side wobble) of disc plate, the thickness of disc plate is uneven.
1. If the runout is more than 0.05 mm {0.002 in} to 10 mm {0.39 in}
from the disc plate edge, an uneven wear occurs on the disc plate because the pad contacts the plate unevenly.
2. If the runout is less than 0.05 mm {0.002 in},
uneven wear does not occur.
The disc plate is deformed by heat.
1. Repeated panic braking may raise the temperature in some portions of disc plate by approximately 1,000 ° C {1,832 °F}.
This results in deformed disc plate.
Due to corrosion, the thickness and friction coefficient of disc plate change.
1. If a vehicle is parked under damp conditions for a long time, corrosion occurs on the friction surface of disc plate.
2. The thickness of corrosion is uneven and sometimes appears like a wave pattern, which changes the friction coefficient and causes a reaction force.
Inspection and repair procedure
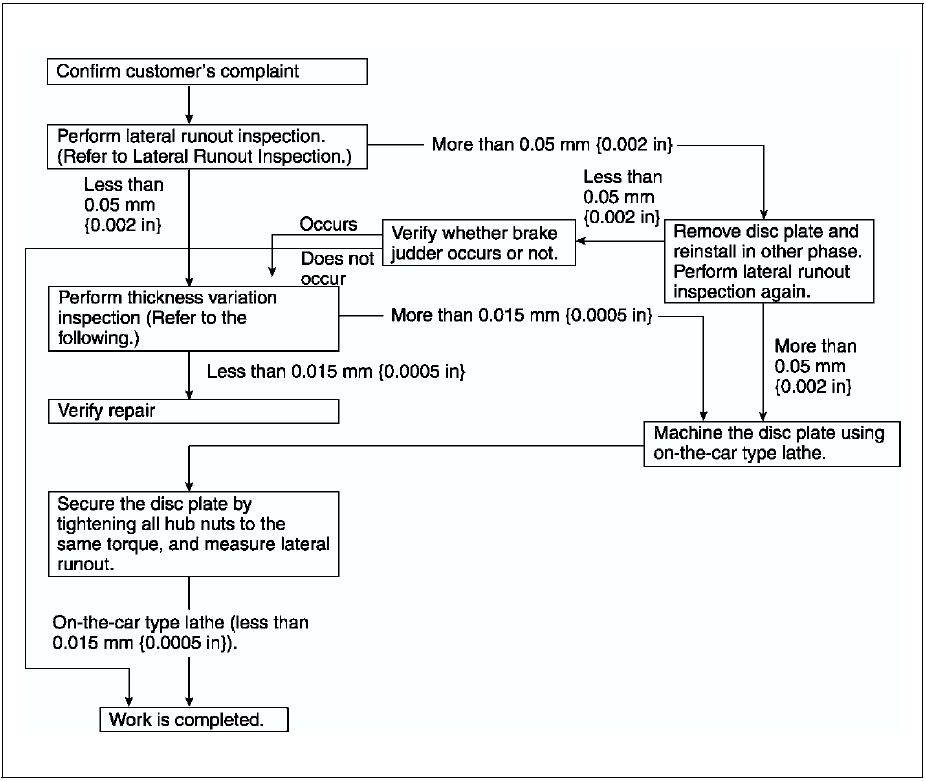
Lateral runout inspection
1. To secure the disc plate and the hub, tighten the hub nuts upside down or insert a washer (thickness 10 mm {0.39 in}
, inner diameter more than 12 mm {0.47 in})
between the hub bolt and the hub nut.
Note
- The component parts of the SST (49 B017 001 or 49 G019 003) can be used as a suitable washer.
2. After tightening all the hub nuts to the same torque, put the dial gauge on the friction surface of disc plate 10 mm {0.39 in}
from the disc plate edge.
3. Rotate the disc plate one time and measure the runout.
Runout limit
0.05 mm {0.002 in}
Thickness variation inspection
1. Clean the disc plate-to-pad friction surface using a brake cleaner.
2. Measure the points indicated in the illustration using a caliper (micrometer).

3. Subtract the minimum value from the maximum, and if the result is not within specification, machine the disc plate using a lathe.
Thickness variation limit 0.015 mm {0.00059 in}
Warning
- Do not exceed minimum disc plate thickness.
Disc Plate Thickness Inspection
Caution
- Excessive runout may result if the disc plate is removed from the vehicle then machined. Machine the disc plate while installed on the vehicle.
1. Measure the thickness of the disc plate.
- If the thickness is not within the specification, replace the disc plate.
Minimum
22 mm {0.87 in}
Minimum thickness after machining using a brake lathe on-vehicle
22.8 mm {0.90 in}
Disc Pad Thickness Inspection
1. Jack up the front of the vehicle and support it with safety stands.
2. Remove the wheel and tires.
3. Verify the remaining thickness of the pads.
Minimum thickness
2.0 mm {0.079 in} min.
4. Replace the pads as a set: right and left wheels, if either one is at or less than the minimum thickness.
 Dual proportioning valve replacement (without abs)
Dual proportioning valve replacement (without abs)
1. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
2. Install in the reverse order of removal.
Dual Proportioning Valve Installation Note
Install the dual proportioning valve so that the R mark fac ...
 Front brake (disc) removal/installation
Front brake (disc) removal/installation
1. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
2. Install in the reverse order of removal.
3. After installation, depress the pedal a few times, rotate the wheel by
hand, and verify that the brake ...
Other materials:
Mazda 6 Service Manual: Gear Shift Indicator (GSI)
The Gear Shift Indicator (GSI) supports you to obtain optimum fuel economy and
smooth driving. It displays the selected gear position in the instrument cluster
as well as notifies the driver to change to the most suitable gear position corresponding
to the actual driving condition.
CAUTIO ...
Mazda 6 Service Manual: Rear wiper motor removal/installation
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the rear wiper arm and blade. (See REAR WIPER ARM AND BLADE
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
3. Remove the liftgate lower trim. (See LIFTGATE LOWER TRIM
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
4. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
5. Install in the revers ...
